PGT. Bioinformatic analysis
BAM file obtained using the Torrent Suite software is transferred to the Ion Reporter software. Aneuploidy detection is performed using an algorithm based on a Hidden Markov Model (HMM).
Hidden Markov Model allows for given model λ = (A, B, π) and sequence O = {o1, ...oT} to calculate the probability P(O/λ) of generating a sequence of observations O = {o1, ...oT} by model λ and most probable sequence Q= {q1, ...qT}. Let them be given sequence of observations O = {o1, ...oT} and model λ = (A, B, π). The Viterbi algorithm is used to select a state sequence Q= {q1, ...qT}, which most likely for a given model P(O/λ) generates the sequence of observations O = {o1, ...oT}. In hidden Markov Model it is possible to monitor only the variables that are influenced by this state. Each state has probability distribution among all possible output values. Therefore, the sequence of symbols generated by HMM provides information about the state sequence.
Ovals represent variables with random values. The random variable x(t) represents the value of the latent variable at time t. The random variable y(t) is the value of the observed variable at time t. Arrows symbolize conditional dependencies. The value of the hidden variable x(t) (at time t) depends only on the value of the hidden variable x(t-1) (at time t-1). It is known as the Markov Property. Although at the same time, the value of the observed variable y(t) depends only on the value of the hidden variable x(t) (both at time t).
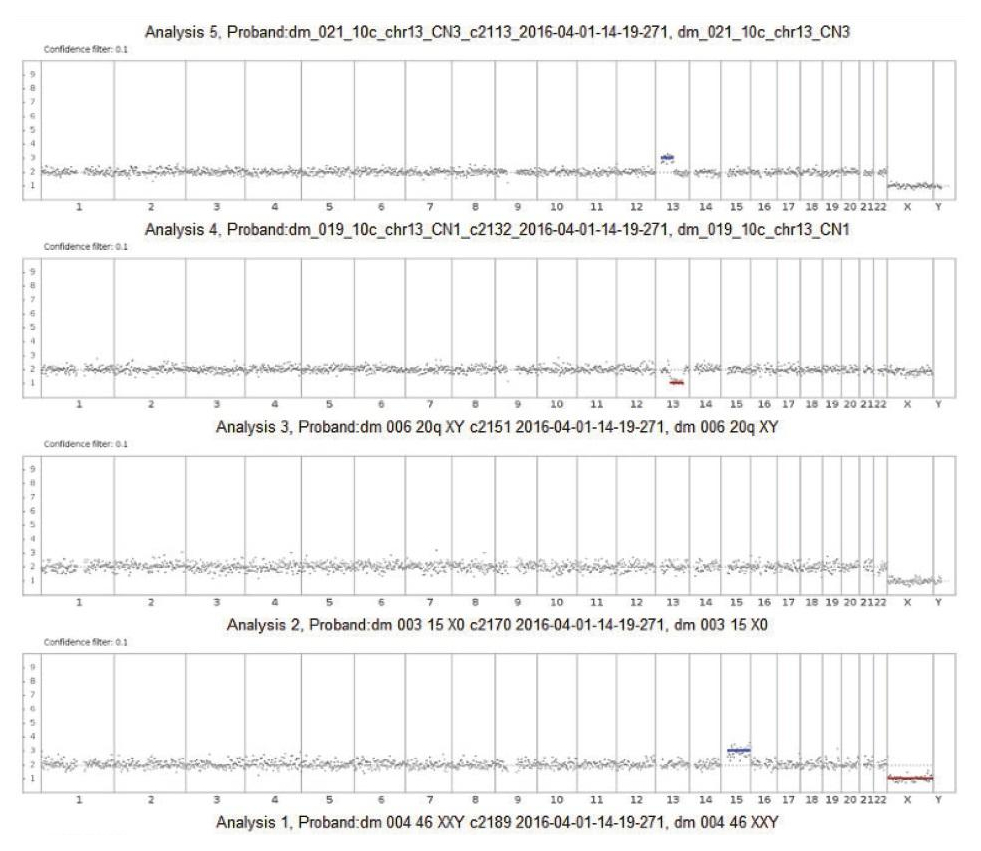
The algorithm uses a statistical model to analyze reads covering the whole genome to predict chromosome copy numbers. Before copy number determination, reads are corrected for GC site errors and compared to a pre-established baseline by analyzing 10 normal male samples in the same manner.
Using 10 samples to calculate the baseline significantly reduces sample-to-sample coverage variability and results in fewer false positives. The use of a given line has been validated using samples in an interlaboratory comparison.
The use of HMM allows one to statistically process all the necessary information about a sample to determine the probability of a specific genomic region deviating from a given ploidy value. Data analysis allows user to provide customized calculation coefficients. Algorithm parameters are configured to process low-coverage whole-genome sequencing data using technical (standard) samples analyzed in duplicate, as well as samples with known aneuploidies. Changing the software metrics allows user to select the sensitivity level (low, medium or high). A highly sensitive protocol allows the analysis of chromosomal segments, as well as the detection of aneuploidies in noisy regions, but at the same time increases the likelihood of a false positive result. Medium sensitivity is the default setting and recommended for use as primary. A low sensitivity protocol is the most «demanding» and detects only regions with extremely high confidence of aneuploidy.