Available on credit
Available on credit
Non–invasive Prenatal Screening
This is a modern method of prenatal testing based on fetal DNA analysis from the venous blood of the mother to calculate the risk of developing chromosomal diseases in the fetus, such as: trisomy, abnormalities in the sex chromosomes.
All NIPT tests: free genetic counselling in the case of a high-risk result
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy
Calculator of the risk of chromosomal abnormalities depending on the age of the expectant mother
Prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal pathology
Chromosomal diseases are hereditary diseases caused by a change in the number or structure of chromosomes.
Numerical chromosomal abnormalities are represented by aneuploidies (trisomies, monosomies, etc.) and polyploidies (triploidy and tetraploidy).
Such anomalies occur, as a rule, due to errors in cell division, when there is an increase and / or decrease in the number of chromosomes in daughter cells or chromosome non-separation. Non-separation occurs as a result of errors during meiosis, fertilization or the first mitosis of the embryo.
The cells resulting from this division are aneuploid, since their chromosome set does not correspond to a typical haploid set of 23 chromosomes.
As a woman’s age increases, the risk of giving birth to a child with numerical chromosome anomalies increases.
The risk increases especially significantly after 35 years.
Structural chromosomal abnormalities occur as a result of changes in the structure of one or more chromosomes and can be divided into unbalanced and balanced abnormalities.
Balanced chromosomal abnormalities are rearrangements due to which a karyotype with a modified set of gene locations within chromosomes or between chromosomes is detected, it differs from the normal karyotype. In most cases, carriers of balanced chromosomal abnormalities are phenotypically normal, but there is a great risk for their offspring to have an unbalanced karyotype.
Unbalanced structural chromosomal abnormalities are characterized by the absence of a chromosomal segment (partial monosomy) or an additional chromosomal segment (partial trisomy) and lead to genomic imbalance. Partial mono- or trisomies are known about almost all chromosomes, but only some of them form clearly diagnosed clinical syndromes.
Chromosomal diseases occupy one of the leading places in the structure of human hereditary pathology.
They are closely associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as spontaneous abortions, stillbirths and are combined with other congenital malformations [1].
Approximately half of fetuses with malformations and spontaneous abortions have chromosomal abnormalities [2].
About 5% of childrenare born with serious birth defects of genetic or partially genetic origin
Defects of partially genetic origin are caused by a combination of genes that puts the fetus at risk in the presence of specific environmental factors [3].
Most chromosomal abnormalities in humans are incompatible with life and lead to termination of pregnancy. Relatively few variants of numerical chromosome abnormalities are compatible with postnatal development: gonosomal trisomies (XXX, XXY, XYY), monosomy X, some autosomal trisomies (21, 18, 13).
Down syndrome
trisomy 21, prevalence at birth 1 in 700 to 1 in 800
Klinefelter syndrome
polysomy X in men, prevalence at birth 1 in 700
Triplo-X syndrome
trisomy X, prevalence at birth 1 per 1 000
Turner syndrome
monosomy X, prevalence at birth 1 in 2 000 girls
Edwards syndrome
trisomy 18, prevalence at birth 1 in 6 500
Patau syndrome
trisomy 13, prevalence at birth 1 in 10 000
Jacobs syndrome
dysomy Y, birth prevalence 1 in 900
XXYY syndrome
polysomy X and Y in males, prevalence at birth 1 in 18 000
[1] Huang L, Jiang T, Liu C. Fetal loss after amniocentesis: analysis of a single center’s 7,957 cases in China. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2015;42:184—7.
[2] Zhu J, Liu H, Tang J, Riaz Khan M, Wang B, Bukhari I. Identification of minor chromosomal defects causing abnormal foetus and spontaneous abortions. Br J Biomed Sci. 2016;73:67–73.
[3] MARCH OF DIMES GLOBAL REPORT ON BIRTH DEFECTS
The non-invasive method of prenatal screening is safe for the mother and fetus, unlike invasive methods of prenatal diagnosis.
The prenatal screening is one of the fastest tests available, the results are provided in just 8 working days from the moment the sample is received
The prenatal screening has a high sensitivity (about 99%) for the determination of trisomies 21, 13, 18.
Methods of prenatal screening and diagnosis
It is possible to diagnose chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus at the stage of intrauterine development. Modern prenatal diagnosis of the fetus includes invasive and non-invasive techniques that can identify most of the congenital and hereditary pathologies of the fetus.
The main method of prenatal screening is screening of the first trimester of pregnancy, that includes biochemical screening and ultrasound examination of the fetus.
The risk of chromosomal pathology within the framework of this method is calculated based on the determination of serum levels of free β-hCG unit, PAPP-A glycoprotein — pregnancy-associated plasma protein A, NT (nuchal translucency), detection of the nasal bone according to ultrasound diagnostics.
- Biochemical screening is carried out at the 10-13th week of pregnancy and is quite strictly limited in time.
- Biochemical screening programs are not very accurate and there is a high percentage of both false positive and false negative results.
- The screening result is not a diagnosis, but an indicator of the individual risk of certain pathologies in the fetus.
In invasive prenatal diagnosis, the material for the analysis is directly embryonic or fetal cells, such as chorionic villi, amniotic fluid or umbilical cord blood. Depending on the pregnancy duration, under the control of ultrasound, the following procedures are carried out:
chorion biopsy — obtaining cells forming the placenta (gestation period — 10-14 weeks);
amniocentesis — puncture of the amniotic bladder with the sampling of a small amount of amniotic fluid (gestation period — 15-18 weeks);
cordocentesis — blood sampling from the umbilical cord of the fetus (gestation period — from the 20th week).
Further, the obtained material is analyzed in various ways:
- Karyotyping
- FISH method
- Chromosomal microarray analysis
The main share of invasive perinatal diagnostics in order to exclude chromosomal diseases is carried out in risk groups formed according to the results of ultrasound and biochemical screening.
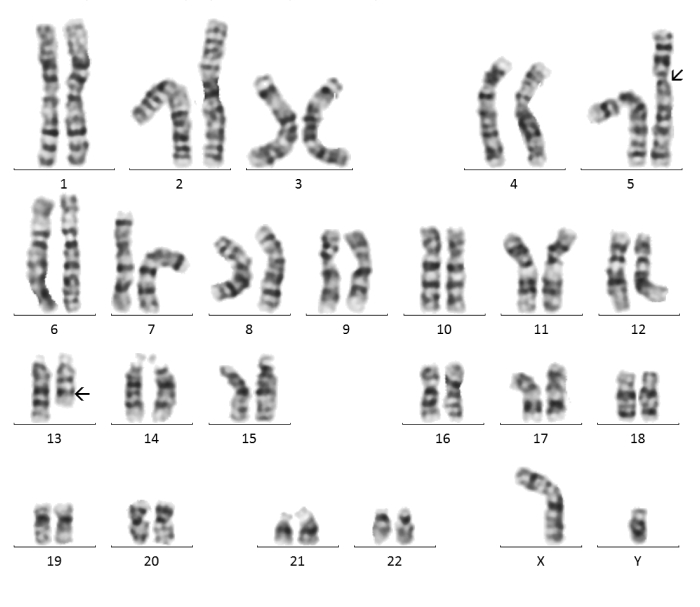
Karyotyping is a cytogenetic testing, the analysis of the human chromosome set, that includes cultivation in order to obtain metaphase cells, followed by the use of differential staining of chromosomes along the length, allowing to detect deviations in the structure and number of chromosomes.
Advantage
The advantage of this method is the ability to determine balanced translocations, marker chromosomes, mosaicism.
Disadvantage
The resolution of cytogenetic research is 5-10 and more million bp, therefore, using this method it is impossible to detect micro-rearrangements within chromosomes, such as microdeletions, microduplications.
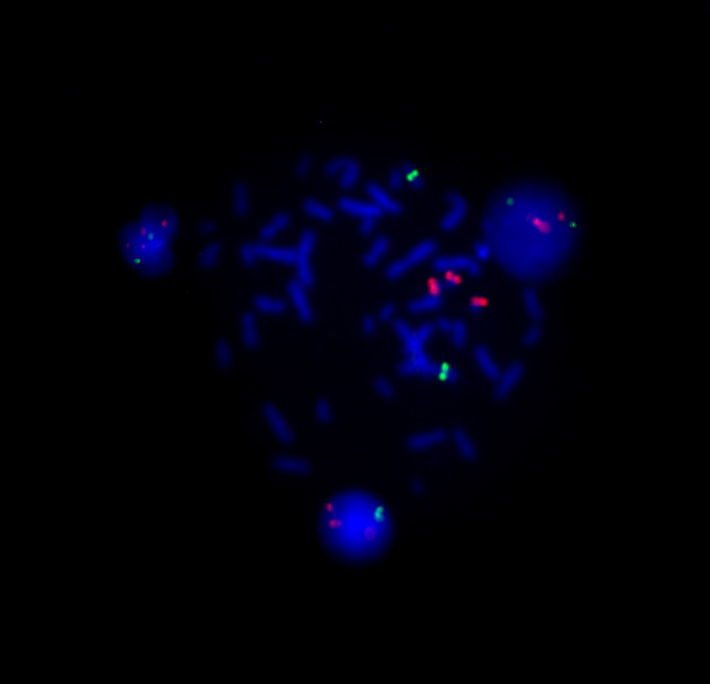
FISH method (fluorescence in situ hybridization) is a molecular cytogenetic method for analyzing genetic material in a cell.
The principle of the FISH method is hybridization — binding of the DNA probe to the chromosomal DNA of the patient’s test sample. FISH technology allows to identify whole chromosomes, chromosome-specific regions or single-copy unique sequences, depending on the labeling techniques used.
Advantage
The FISH method is a quick way to exclude the most common anomalies in the 13th, 18th, 21st pair and anomalies of the X and Y sex chromosomes.
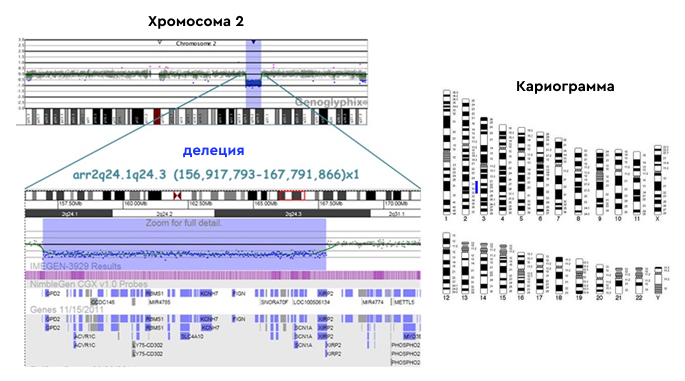
Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) is a diagnostic test that detects clinically significant large chromosomal abnormalities (aneuploidies) as well as submicroscopic copy number variations (microdeletions/microduplications) throughout the genome.
Chromosomal microarray analysis is the gold standard for detecting deletions and duplications throughout the genome.
Advantages of the method
- high resolution (more than 1000 times compared to karyotyping);
- simultaneous examination of thousands of regions of all chromosomes;
- the possibility of quantitative determination of microscopic chromosomal abnormalities: aneuploidy (including mosaicism), unbalanced translocations, marker chromosomes;
- submicroscopic abnormalities: microdeletion and microduplication syndromes;
- а также несбалансированных субтеломерных перестроек;
- the ability to detect uniparental disomies;
- research automation;
- objectivity and high informativeness of the results obtained.
While performing CMA, the stage of cell cultivation is excluded, that is necessary for the cytogenetic analysis performance, it contributes to a faster result.
Disadvantage
This method does not exclude the presence of balanced chromosomal rearrangements (reciprocal translocations and insertions, inversions, Robertsonian translocations), a low level of mosaicism (less than 20%), unbalanced rearrangements beyond the matrix resolution limit, point mutations, as well as certain polyploidies.
Limitations of invasive methods
All of these testings are highly accurate methods, their accuracy is about 99%.
However, invasive diagnostics is associated with the risk of complications, such as
- spontaneous miscarriage,
- obstetric bleeding,
- fetal damage,
- infection that may occur during the sampling of the material.
Taking into account the professionalism of the doctor, the technical equipment of the clinic, the patient’s health, compliance with all norms and rules, the risk of pregnancy loss is reduced to 2%.
And this indicator is not higher than that of other pregnant women. Meanwhile, the result obtained is extremely important for the prognosis of the health of the unborn child.
Over the past decade, with the development of genetic technologies, new methods of prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities have appeared.
Non–invasive Prenatal Screening (NIPT)
Non-invasive prenatal test (NIPT) is a screening genetic method for detecting fetal chromosomal abnormalities.
During pregnancy, cell free fetal DNA (cfDNA) is released from the placenta and circulates in the maternal bloodstream. As a result, maternal blood contains a mixture of circulating fetal and maternal DNA. NIPT directly measures the amount of this cfDNA and can detect the slightest deviations in the ratio of fetal chromosomes. After bioinformatic data analysis, the risk of aneuploidy for certain chromosomes is calculated.
NIPT has become available as a much more accurate screening test for the most common chromosomal abnormalities, what significantly reduced the need for invasive tests.
NIPT does not require intervention in the body what makes the non-invasive test a safe, very convenient and simple method.
Another advantage of the non-invasive test is its high sensitivity:
about 99%sensitivity for the 21st, 13th, 18th pairs of chromosomes
NIPT is performed from the 10th week of pregnancy and does not require special preparation for the delivery of biomaterial.
- All pregnant women who want to get additional information about the health of the unborn baby
- Pregnant women over the age of 35
- Pregnant women whose screening of the 1st or 2nd trimester showed an increased risk of chromosomal pathology
- Pregnant women who have contraindications to invasive diagnostics (threat of pregnancy loss, fever, infections, tendency to bleeding)
- Pregnant women, if during previous pregnancies the fetus was diagnosed with Down syndrome, Edwards, Patau or other chromosomal pathologies
- Pregnant women who have had cases of intrauterine fetal death, pregnancy loss
How NIPT is conducted
Fetal DNA is extracted from the venous blood of the mother, which is found in the blood of a pregnant woman and can make up to 10% of the total DNA volume. The resulting DNA is analyzed by next generation sequencing, the chromosomal ratio of cfDNA is calculated, and after processing with special algorithms, the most accurate result is generated regarding the presence of common genetic abnormalities in the fetus.
What pathologies are determined by NIPT
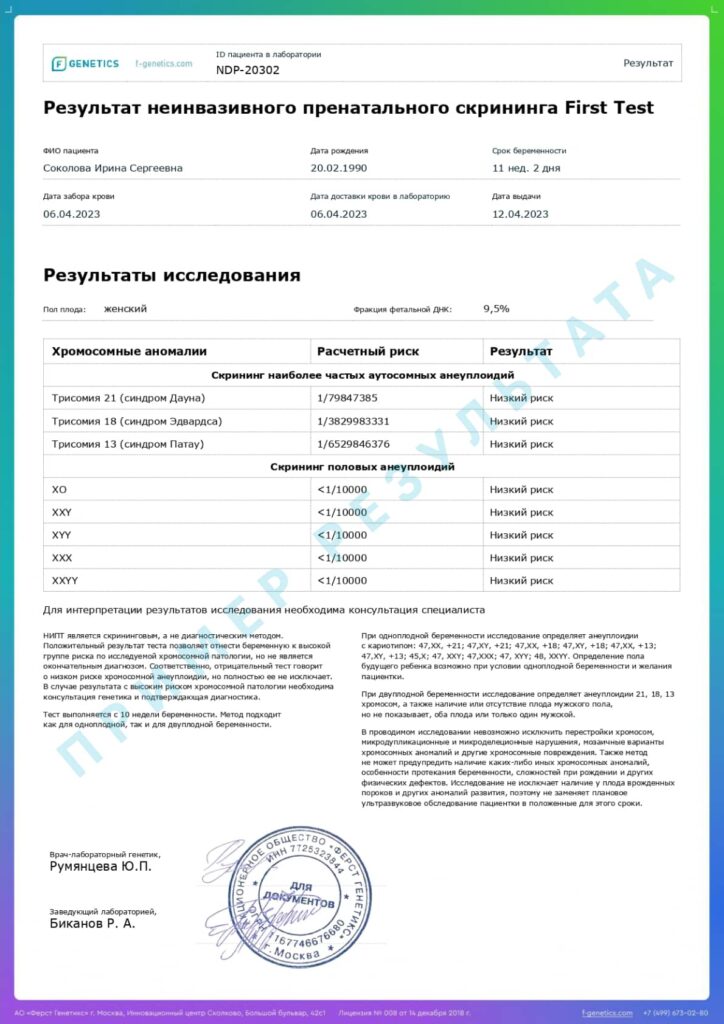
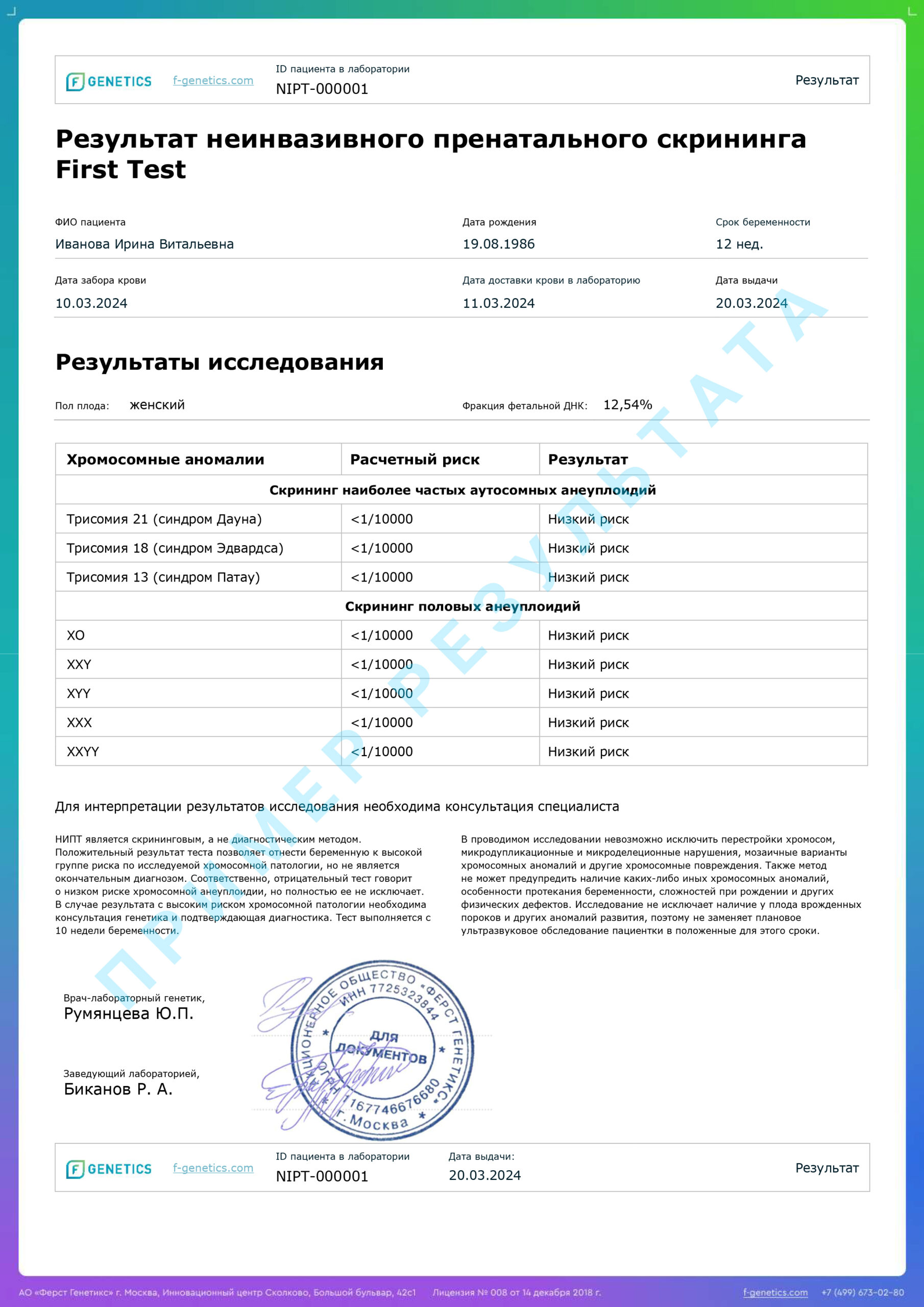
The prenatal screening report contains a clear, easily interpreted result about the presence of a high or low risk of chromosomal pathology.
These include:
- trisomy 21 (Down syndrome),
- trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome),
- trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome).
The accuracy of NIPT is quite high, but differs in the analyzed chromosomes.
In addition to three autosomes, NIPT also determines the pathology of two sex chromosomes: X and Y, allowing to identify the following sex chromosome aneuploidies:
- XO — X — Turner monosomy syndrome,
- XXX — triple X syndrome,
- XXY — Klinefelter syndrome,
- XYY — Jacobs syndrome,
- XXYY syndrome.
The non—invasive prenatal screening makes it possible to calculate the risks for the most common chromosomal pathologies.
Results of the non—invasive prenatal screening
The prenatal screening report contains a clear, easily interpreted result about the presence of a high or low risk of chromosomal pathology.
Low risk
Absence of chromosomal pathology with an accuracy of more than 99%.
High risk
There is an increased risk of a chromosomal abnormality. All high—risk results should be further investigated by invasive methods (chorion biopsy, amniocentesis).
No result
If the placental DNA level in the sample is below 3.5%, then a second sampling may be required, since a low fraction of fetal DNA is potentially capable of causing a false negative result.
The testing is not carried out in the following cases:
- less than 10 weeks gestation of pregnancy at the time of blood sampling for testing;
- oncological diseases;
- organ or bone marrow transplantation, stem cell therapy;
- allogeneic blood transfusion within the previous year;
- therapy with human serum albumin and/or exogenous DNA cells within the last four weeks;
- heparin therapy within 24 hours before sampling;
- the death of one of the fetuses during multiple pregnancy (earlier than 8 weeks after the discovery of a dead fetus);
- pregnancy with more than two fetuses;
- pregnancy with two fetuses using donor programs (donor eggs, surrogate motherhood).
Safe
The non—invasive method of prenatal screening is safe for the mother and fetus, unlike invasive methods of prenatal diagnosis.
Fast
The prenatal screening is one of the fastest tests available, the results are provided in just 8 working days from the moment the sample is received.
Accurate
The prenatal screening has a high sensitivity (about 99%) for the determination of trisomies 21, 13, 18.
How to get NIPT?
THE FASTEST WAY: GIVE BLOOD IN THE LABORATORIES OF OUR PARTNERS
Select a laboratory that is convenient for you on the map during the order process.
A CONVENIENT WAY: CALL A COURIER
Call a courier who will bring you a blood collection kit.
Give some blood into the tube that you received in the kit at any site where blood is taken at your location (laboratories, clinics, medical offices).
Blood sampling should be carried out in strict accordance with the instructions attached in the kit.
Be sure to indicate your full name and the date of blood sampling on the tube.
Store the tube in strict accordance with the instructions attached in the kit, before the courier arrives.
Call the number again and give the courier the kit and the tube with blood. The courier will take the tube to the laboratory.
Non-invasive prenatal screening at First Genetics laboratory
Specialists
Years of experience in genetics, laboratory diagnostics and bioinformatics
Confidentiality
All data is strictly confidential and cannot be passed on to third parties
Consulting
You can get an online consultation regarding the results of test
Security
Extensive control at each stage of testing
Free delivery
Free delivery of biomaterial across Russia
Charities
Email info@f-genetics.com for information
All NIPT tests: free genetic counselling in the case of a high-risk result
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy
- Down syndrome
- Edwards syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Trisomy-X
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Jacobs syndrome (disomy - Y)
- XXYY syndrome
- Gender determination (optional)
- Free invasive diagnostics in the case of a high-risk result
- In case of a double pregnancy